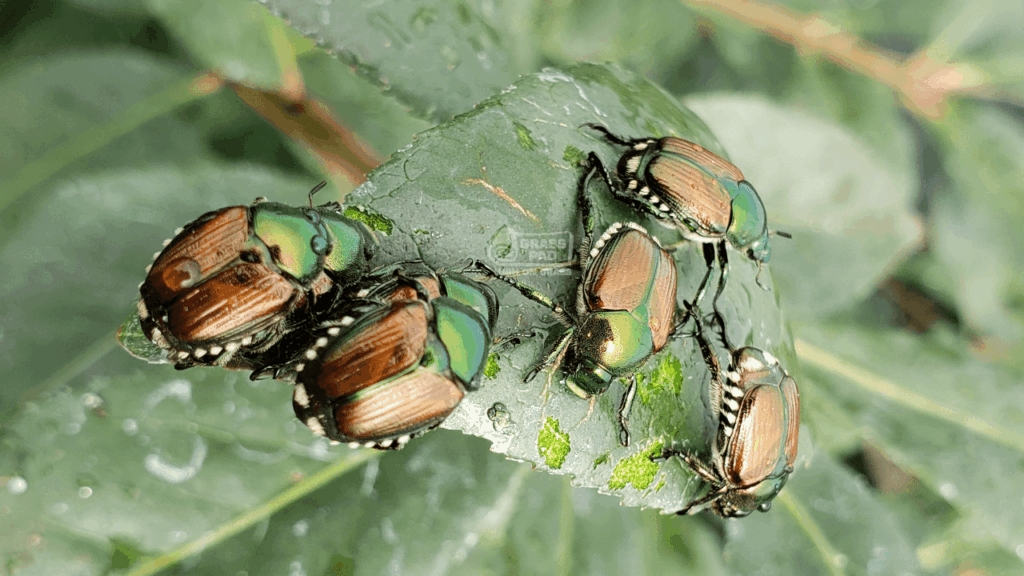
Japanese beetles are this generation’s destroyer of the landscape. These little metallic militants appear in swarms in July and last for months. They are feeding on their favorite plants and when those are decimated, they move on to the next. They love roses, fruit trees, vegetables and especially linden trees. Reducing the Japanese beetle population requires a different strategy than the traditional preventative control for white grubs. Protecting our favorite roses and fruit trees will involve treatments for adult beetles as well as the grub stage.
Best Control for Japanese Beetles
Both as adults and as grubs, Japanese beetles are destructive plant pests. Adults feed on plant foliage, mate, and lay eggs, and the carnage continues when the next generation hatch. Japanese beetle larvae feed on turf grass roots. Unlike the traditional masked chafer, May beetle, and June Bug, the Japanese beetle lays eggs and has multiple hatchings. Effective Japanese beetle control will now require multiple phases of curative and preventive applications.

Curative Controls for Beetles in Trees and Shrubs
Swarms of adult Japanese beetles are more of a challenge to control. The best method is to spray them with Cyonara Lawn & Garden, Bifenthrin or Malathion. These products are compatible with most fruit and vegetable crops as well as landscape plants. If you discover just a few beetles, they can easily be picked off and dropped into a bucket of soapy water.
Cyonara Lawn & Garden is a broad-spectrum insect control product. In addition to Japanese Beetles, Cyonara Lawn & Garden kills spider mites, fleas, aphids, fire ants, chinch bugs and more.
Prevent Japanese Beetle Damage in Trees & Shrubs
Preventative treatment for adult beetles on shrubs and trees* begins in early May with a soil drench application of Dominion Tree & Shrub Insecticide. A direct soil application of Dominion Tree & Shrub around trees and shrubs should be applied before Mother’s Day to provide systemic control with up to twelve-month residual. The insecticide is absorbed into the plant, killing any insect that eats the leaves or bark. This product not recommended for use around linden trees.
* Be Safe! Always read the label before using any pesticide. Follow all label instructions.

Curative Control for Japanese Beetle Grubs
The Hail Mary is applying Quick Kill Grub Control in the middle of September as Long Lasting Grub Control has faded. Quick Kill is the only effective contact-kill for white grubs. It is very fast acting with a short active life. It’s important to water heavily after application to help penetrate any thatch in the yard. If the problem recurs, you can apply a second or third dose of Quick Kill Grub Control.
Prevent Japanese Beetle Grub Damage
As the Japanese Beetles move through their life cycle, they will start to lay eggs in the grass. To prevent grub damage, treat the yard with Long Lasting Grub Control in early summer before the lawn goes under heat stress. This preventative treatment is designed to be applied before a potential grub problem develops. It is normally applied in late June to early July and kills the baby grubs as they hatch. Long-Lasting Grub Control will stay active in the lawn for about ninety days.
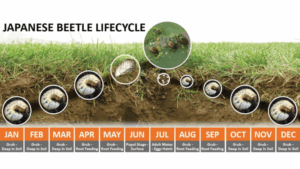
Why Japanese Beetles Do So Much Damage?
Japanese beetles reproduce at very high rates, unlike their cousin, the masked chafer (the “June bug”) that lives only a few weeks. The adult Japanese beetle lives for months to eat, mate, and lay eggs recurrently. Once the eggs start to hatch into grubs, continuous waves of ravenous white grubs begin feeding on the roots of your grass.
Why do Japanese Beetles Swarm?
Plant odors attract both sexes to potential food sites. Japanese beetle feeding produces odors which act as pheromones to attract other Japanese beetles to the area to feed and mate. Pheromones are chemical odors used by insects to communicate.
Where Did Japanese Beetles Come From?
Originally from Asia, Japanese beetles were brought over to the United States in 1917 into New Jersey. Currently the insect can be found in all states east of the Mississippi River, except Florida and Louisiana.
About Japanese Beetle Pheromone Traps
We discourage the use of beetle pheromone traps; however, beetle traps do work in that they capture adult beetles. However, placement is critical. DO NOT place the traps near any plant material you do not want the beetles feeding on. Although the trap is quite effective in attracting the beetle, only about 70 percent of the beetles end up in the trap. In addition, pheromone traps attract more beetles to your property than would have visited your property naturally. Research has shown that putting the traps on the perimeter of the property well away from valuable plantings or vulnerable crops may be the best use of the traps. Traps work better if you also get your neighbors to set out traps. Use a community-wide approach of 25 to 50 traps per square mile.